Ecology in Isfahan
| Isfahan city |
|---|
 |
| City
|
| Places
|
|
The ecological environment of Isfahan, Iran, reflects many interrelated factors, such as wildlife, climate, topography, irrigation, farming, and the human population.
Geography
The average altitude in the Isfahan city area is 1,607 m (5,272 ft) above sea level (compared to 1563 meters for the larger Isfahan province). Mount Soffeh is the highest point in the city at 2216 meters above sea level.
The city of Isfahan covers an area of 550 square kilometers and is surrounded by an additional 136 square kilometers in suburbs.
Biodiversity
Gavkhouni, an ancient marsh with highly saline water and uniquely adapted wildlife, is located in the eastern part of the city.
The Isfahan Department of Environment was established in 1972 to conserve biodiversity.[1] Two national animal conservation parks are nearby: Kolah Ghazi Park in the southeast, and Ghamishloo park in the northwest.
Water
Some 10 kilometers of canals and aqueducts crisscross the area. 14 water tunnels service Isfahan. Other water projects related to the city are the Yazd Water Transfer Pipeline, the Koohrang river tunnels, Kouhrang 2 Hydroelectric Power Station, Kouhrang 1 Dam, and Kouhrang 3 Dam.[2]
The city relies on wells and the Zayanderud dam as its main sources of potable water.
Drought

Much of Isfahan's water management effort is devoted to combating drought. For example, the city has switched to xeriscaping lawns in a response to water scarcity.[3] By 2020, 52% of city green space (1820 hectares) was maintained with micro-irrigation, a low-pressure water system designed to minimize water use.[4]
Waste
Isfahan's population of 1,980,000 people creates almost 864 tons of waste daily, or 436 grams per citizen. The Isfahan compost fertilizer factory recycles 650 tons of waste each day and ranks first in the country.[5]
Of the city's 5200 hectares of green space, 35% is irrigated using reclaimed wastewater. The city's main wastewater treatment plants are located in Sepahan Shahr (south) and Shahin Shahr (north).
Air quality
In 2013 Isfahan had only two days of clean air. 13 sensor stations measure its air quality.
-
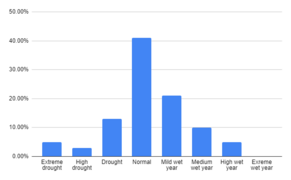 1972 to 2009 abundance percentage of years of drought and wet periods data isfahan atlas
1972 to 2009 abundance percentage of years of drought and wet periods data isfahan atlas -
 Isfahan city greenspace share atlas data 2020
Isfahan city greenspace share atlas data 2020 -
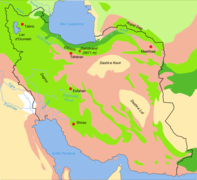 Map iran biotopes simplified-fr
Map iran biotopes simplified-fr -
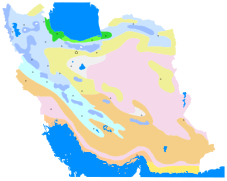 Iran climate map
Iran climate map
Further reading
- City green space program view on sustainability: Case study district 3 of Isfahan.[6]
See also

References
- ^ "about the department of environment isfahan province".
- ^ "manabe ab" (PDF). Atlas for Isfahan. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-10-08. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ "شناسايي گونه هاي گياهي متناسب با اقليم اصفهان". new.isfahan.ir. Archived from the original on 2020-10-08. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ "مدیریت منابع برای فضای سبز اصفهان در اولویت برنامهریزی شهری". ایمنا (in Persian). 2020-10-05. Archived from the original on 2020-10-08. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ "اطلس اصفهان". new.isfahan.ir. Archived from the original on 2020-09-22. Retrieved 2020-10-07.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-10-08. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
External links
- Department of Natural Resources and Watershed Management of Isfahan
- Isfahan Department of Environment
- "مادی ها و انهار | سازمان پارکها و فضای سبز شهرداری اصفهان". park.isfahan.ir. Retrieved 2022-03-29.
- "All Location on map | سازمان پارکها و فضای سبز شهرداری اصفهان". park.isfahan.ir. Retrieved 2022-03-29.
























